信号驱动的IO
信号驱动的IO是一种半异步的IO模型。使用信号驱动I/O时,当网络套接字可读后,内核通过发送SIGIO信号通知应用进程,于是应用可以开始读取数据。
具体的说,程序首先允许套接字使用信号驱动I/O模式,并且通过sigaction系统调用注册一个SIGIO信号处理程序。当有数据到达后,系统向应用进程交付一个SIGIO信号,然后应用程序调用read函数从内核中读取数据到用户态的数据缓存中。这样应用进程都不会因为尚无数据达到而被阻塞,应用主循环逻辑可以继续执行其他功能,直到收到通知后去读取数据或者处理已经在信号处理程序中读取完毕的数据。
设置套接字允许信号驱动IO的步骤如下:
注册SIGIO信号处理程序。(安装信号处理器)
使用fcntl的F_SETOWN命令,设置套接字所有者。(设置套接字的所有者)
使用fcntl的F_SETFL命令,置O_ASYNC标志,允许套接字信号驱动I/O。(允许这个套接字进行信号输入输出)
信号驱动的IO内部时序流程如下所示: 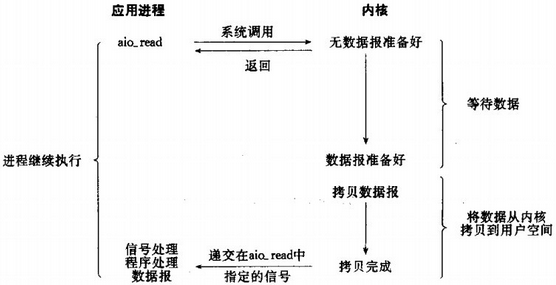
之所以说信号驱动的IO是半异步的,是因为实际读取数据到应用进程缓存的工作仍然是由应用自己负责的,而这部分工作执行期间进程依然是阻塞的,如上图中的后半部分。而在下面介绍的异步IO则是完全的异步。
示例程序:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
#include <termios.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/signal.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#define BAUDRATE B9600
#define MODEMDEVICE "/dev/ttyACM0"
#define _POSIX_SOURCE 1 /* POSIX compliant source */
#define FALSE 0
#define TRUE 1
volatile int STOP=FALSE;
void signal_handler_IO (int status); /* definition of signal handler */
int wait_flag=TRUE; /* TRUE while no signal received */
char buf[255];
int fd, res;
main()
{
//int fd,c, res;
int c;
struct termios oldtio,newtio;
struct sigaction saio; /* definition of signal action */
//char buf[255];
/* open the device to be non-blocking (read will return immediatly) */
fd = open(MODEMDEVICE, O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY | O_NONBLOCK);
if (fd <0) {perror(MODEMDEVICE); exit(-1); }
/* install the signal handler before making the device asynchronous */
saio.sa_handler = signal_handler_IO;
//saio.sa_mask = 0;
/* Signals blocked during the execution of the handler. */
sigemptyset(&saio.sa_mask);
sigaddset(&saio.sa_mask, SIGINT);
saio.sa_flags = 0;
saio.sa_restorer = NULL;
sigaction(SIGIO,&saio,NULL);
/* allow the process to receive SIGIO */
fcntl(fd, F_SETOWN, getpid());
/* Make the file descriptor asynchronous (the manual page says only
O_APPEND and O_NONBLOCK, will work with F_SETFL...) */
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, FASYNC);
tcgetattr(fd,&oldtio); /* save current port settings */
/* set new port settings for canonical input processing */
newtio.c_cflag = BAUDRATE | CRTSCTS | CS8 | CLOCAL | CREAD;
newtio.c_iflag = IGNPAR | ICRNL;
newtio.c_oflag = 0;
//newtio.c_lflag = ICANON;
newtio.c_cc[VMIN]=1;
newtio.c_cc[VTIME]=0;
tcflush(fd, TCIFLUSH);
tcsetattr(fd,TCSANOW,&newtio);
/* loop while waiting for input. normally we would do something
useful here */
while (STOP==FALSE)
{
//printf(".\n");
usleep(100000);
/* after receiving SIGIO, wait_flag = FALSE, input is available
and can be read */
if (wait_flag==FALSE)
{
res = read(fd,buf,255);
buf[res]=0;
printf(":%s:%d\n", buf, res);
//if (res==1) STOP=TRUE; /* stop loop if only a CR was input */
wait_flag = TRUE; /* wait for new input */
}
}
/* restore old port settings */
tcsetattr(fd,TCSANOW,&oldtio);
}
/***************************************************************************
* signal handler. sets wait_flag to FALSE, to indicate above loop that *
* characters have been received. *
***************************************************************************/
void signal_handler_IO (int status)
{
printf("received SIGIO signal.\n");
//wait_flag = FALSE;
res = read(fd,buf,255);
buf[res]=0;
printf(":%s:%d\n", buf, res);
}